WHO’s Warning
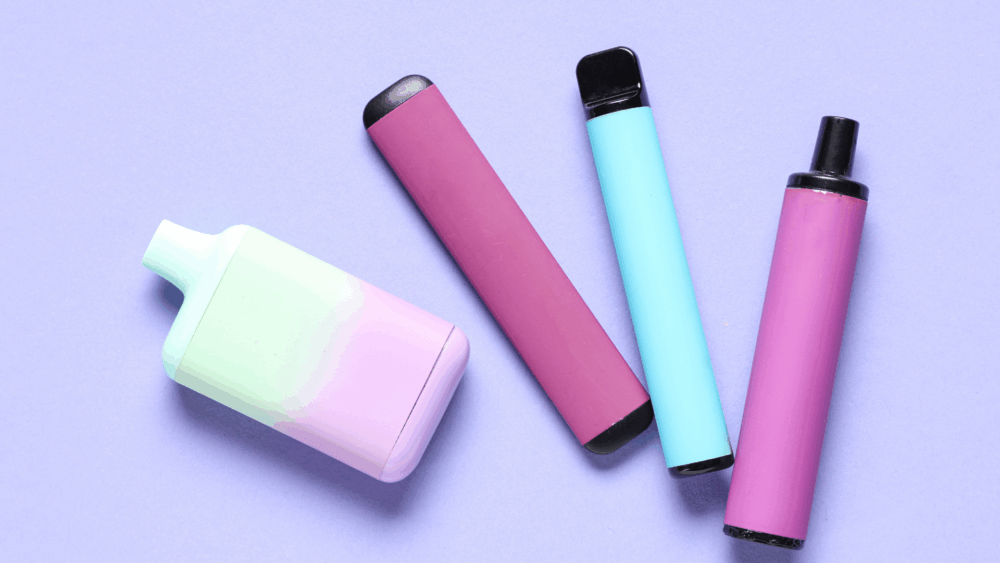

The World Health Organization is sounding the alarm: e-cigarettes are contributing to a new wave of nicotine addiction among young people. According to their estimates, at least
In this context, it is essential to distinguish between addictive psychoactive substances and natural wellness products like CBD. In this article, we clarify what the WHO is denouncing, and why properly formulated hemp-based products do not fall into the logic of addiction.
Nicotine Addiction on the Rise
The World Health Organization warns of an alarming wave of nicotine addiction among young people. According to recent figures, nearly 15 million adolescents now use e-cigarettes worldwide. These products, often presented as a safer alternative to tobacco, nevertheless reinforce addiction, especially among the youngest.
The WHO denounces a well-honed strategy by the tobacco industry: targeted marketing, social media, and influencers. Adolescents are exposed to content that normalizes nicotine use, sometimes from childhood.
"These products make children addicted to nicotine earlier and risk undermining decades of progress," said Étienne Krug, WHO Director.
Global Decline in Smoking, but a New Threat
Despite these worrying figures, the world globally smokes less than twenty years ago. The number of smokers has decreased from 1.38 billion in 2000 to 1.2 billion in 2024, a significant drop.
However, this improvement is now undermined by the rise of new nicotine-based products, such as e-cigarettes or puffs, which are attracting a new generation of users.
WHO Director-General, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, calls on governments to act faster and more firmly to prevent a new public health crisis related to addiction.
CBD and Nicotine: Two Very Different Worlds
Given this rise in addiction, it is important to distinguish between the substances involved.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive compound derived from hemp. Unlike nicotine or THC, it causes neither nervous system stimulation nor addiction.
More and more consumers are turning to CBD for wellness, whether in the form of
CBD oils
,
creams
, or herbal teas. These products do not contain nicotine and do not induce addiction, which radically distinguishes them from tobacco-based products.
Towards more Conscious Consumption
The WHO's warning highlights a crucial issue: the need to better inform young people and promote healthier consumption habits.
From this perspective, CBD is part of a natural and responsible wellness approach, as opposed to products that foster addiction.
Understanding the difference between nicotine, THC, and CBD helps to better grasp the effects and risks associated with each substance.
Informing, educating, and encouraging vigilance remain the best weapons against addiction, whatever its form.
The WHO's warning highlights the importance of collective vigilance against the tobacco industry's strategies and the normalization of nicotine among young people. While e-cigarettes are still presented as an alternative to combustion, their unregulated use now raises real public health concerns.
At Cannahouse, we want to clarify that the purpose of this article is not to present CBD as a healthier alternative to nicotine, but rather to inform about the public health issues raised by this WHO report.
Hemp-based products, such as
CBD oils
, are part of a wellness and transparency approach. The key is to stay informed, understand, and consume responsibly.